
Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Celery root knot nematode (254)
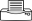
Summary
- Worldwide distribution. In tropics and sub-tropics. Apart from celery, common vegetable hosts are beans, capsicum, carrot, cucumber, eggplant, ginger, lettuce, potato, tomato, and yam; common fruit crop hosts are melon, papaya, and pineapple, and many ornamentals. An important nematode disease.
- Above ground, leaves yellow with brown margins, wilt and die early; below ground, galls on roots.
- Eggs in soil hatch, young larvae enter root behind the tip, and cause cells to swell and galls to form.
- Cultural control: important - pasteurise nursery soil or use soil-less mixes; add organic matter; solarise soil for 4-6 weeks under black plastic; keep soil well watered and use mulch; collect and burn trash after harvest; fallow land for 4-6 months; rotate with e.g., more tolerant maize, peanuts, onions, brassicas, chilli, sweetpotato, or sorghum x Sudan grass hybrids, green panic grass, or grow marigold cover crops.
- Chemical control: none recommended.
Common Name
Root knot nematode. Also, see Fact Sheet no. 127.
Scientific Name
Meloidogyne species. Meloidogyne hapla, Meloidogyne incognita, and Meloidogyne javanica all attack celery.
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests and Pathogens
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2019. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition