
Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Taro leaf blight (014)
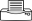
Summary
- Worldwide distribution. On taro and some other edible aroids. An important disease.
- A blight caused by a water mould, an oomycete, not a fungus. Leaves die early and corm yields are low.
- Corm infections occur at harvest, resulting in firm, brown rots.
- Spread is in wind-driven rain, and “tops” for planting.
- Cultural control: isolate gardens, far from those with leaf blight, preferably >500 masl; avoid planting suckers with leaves attached; inspect regularly, and remove infected leaves; harvest when leaves are dry; store corms in plastic bags (or plastic-lined boxes); tolerant (bred) varieties are main method of control.
- Chemical control: copper, chlorothalonil, or mancozeb (protectants); metalaxyl or phosphorous acid (systemics).
Common Name
Taro leaf blight
Scientific Name
Phytophthora colocasiae
AUTHORS Helen Tsatsia & Grahame Jackson
Photos 1&6 Brooks FE (2005) Taro leaf blight. The Plant Health Instructor. DOI:10.1094/PHI-I-2005-0531-01. Diagram Vickie Brewster.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests and Pathogens
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2019. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests & Pathogens - Mini Fact Sheet Edition