
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Bean lace bug (253)
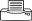
Summary
- Widespread distribution (but not Africa). On beans, bele, breadfruit, eggplant, Hibiscus, and many other hosts. CABI lists soursop and sweetpotato.
- Nymphs and adults use piercing mouthparts to feed on leaves causing large brown patches on beans, and white spots and whitish-yellow patches on eggplant. Brown faecal spots are present on the underside of leaves.
- Probably not of economic importance, except in dry weather, when natural enemies low.
- Natural enemies: parasitoid wasps, assassin bugs, lacewing larvae, ladybird beetles, pirate bugs, and more.
- Cultural control: create conditions for healthy growth - ensure adequate manures or fertilizer, and water.
- Chemical control: use soap, white or horticultural oils,or PDPs: neem, derris, chilli or pyrethrum. Alternatively, use synthetic pyrethroids, although they are likely to kill natural enemies.
Common Name
Bean lace bug, cotton lace bug
Scientific Name
Corythucha gossypii
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community. Photo 3 Mike Furlong, University of Queensland, Brisbane.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition