
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Cabbage diamondback moth (020)
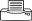
Summary
- Worldwide distribution. Members of the cabbage (brassica) family, e.g., head cabbage, Chinese cabbage, radish, cauliflower and broccoli; Amaranthus and watercress. An important pest.
- Eggs, yellow, small, laid singly. Young larvae mine leaves; larger ones leave waxy windows and holes. If touched, larger ones wiggle backwards, and fall down on silk threads.
- Natural enemies: wasp parasitoids, especially Cotesia (see Fact Sheet no. 287) and Diadegma (see Fact Sheet no. 285).
- Cultural control: inspect nurseries and crops regularly; remove larvae; use trap crops, e.g., mustards or Chinese cabbage (Bok Choy), but destroy trap crop before eggs hatch.
- Chemical control: in household plots, PDPs (chillies, neem, derris, pyrethrum to safeguard natural enemies); in commercial plots, grow under nets; use Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) sprays against caterpillars when young. Avoid pyrethroids and organophosphates.
Common Name
Diamondback moth
Scientific Name
Plutella xylostella
AUTHORS Grahame Jackson & Mike Furlong
Photos 1&2 Graham Walker, Plant and Food Research, Auckland, New Zealand. Photo 4 Richard Markham, ACIAR, Canberra. Photo 4 Jack Kelly Clark, US Statewide IPM Project. Photos 5,7-9) Mike Furlong, University of Queensland, Australia. Photo 6 Mani Mua, SPC, Sigatoka Research Station, Fiji.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition