
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Ginger soft rot (162)
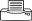
Summary
- Worldwide distribution. In tropics and sub-tropics. On ginger, taro, giant taro, Xanthosoma, beans and capsicum (see Fact sheet no. 44). Many kinds of seedlings are susceptible to damping-off disease in the nursery (see Fact Sheet No. 47).
- A water mould, an oomycete, not a fungus, living in soil on remains of crops, weeds, or as resistant spores.
- Swimming spores infect roots, buds on rhizome or the stems of shoots. Stems collapse, and leaves yellow and die. Patches of yellow develop in the field.
- Spread occurs in soil water to neighbouring plants, and long distances in “seed” used for planting.
- Cultural control: raised beds with deep ditches to drain soil and isolate disease outbreaks; clean “seed” from healthy crops; weed; 3-4-year crop rotation.
- Chemical control: metalaxyl and phosphorous acid (possibly), but unlikely to be economic.
Common Name
Soft rot, rhizome rot
Scientific Name
Pythium spp. Pythium myriotylum is the most serious of the species on ginger.
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Photo 1 Robert Fullerton, Plant & Food Research, Auckland, New Zealand.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition