
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Onion thrips (117)
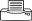
Summary
-
Worldwide distribution. On onions, a preferred host, but infestations also occur on onion relatives, beans, brassicas, carrot, cotton, cucurbits, legumes, papaya, pineapple, potato, tobacco, tomato and many ornamentals. At least 25 plant families are infested.
-
Thrips pierce cells and suck up the contents, leaving white specks. They spread viruses.
-
Spread is by flight from
weeds, on air currents, and in the trade in bulbs.
-
Natural enemies. many predators.
-
Cultural control: nurseries far from field crops; inspect transplants carefully; avoid planting new crops next to old, and not downwind; remove
weeds and “volunteers”; mulch; use yellow sticky cards to check for thrips; collect plant trash and burn after harvest; 2-3-year rotations.
-
Chemical control: soap, white or horticultural oils, neem or spinosad; note, thrips have developed resistance to many pesticides, which will kill natural enemies.
Common Name
Onion thrips
Scientific Name
Thrips tabaci
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Information from CABI (2014) Thrips tobaci (onion thrips) Crop Protection Compendium (https://www.cabi.org/cpc/). Photos 1&2 Rehan Silva University of Queensland.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition