
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Taro root rot (044)
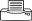
Summary
- Worldwide distribution. Several types. On taro and Xanthosoma, but also on bean, capsicum, ginger, peanuts and pineapple, and weeds; causes a damping-off disease (see Fact Sheet No. 47). An important disease.
- A water mould, an oomycete, not a fungus. Worse in wet soils.
- Roots infected; leaves wilt, become stunted, with only one or two leaves remaining. Corm yields are low; post-harvest rots occur.
- Cultural control: clean “tops” of roots and soil; avoid areas that flood, or where water remains for several days; plant on raised beds with surrounding ditches; grow e.g., Mucania or Pueraria before taro to build organic matter content of the soil; add lime (20g/m2) to increase calcium; >3-year crop rotation; collect debris and burn after harvest.
- Chemical control: none recommended.
Common Name
Taro root rot, cocoyam root rot, Pythium root rot of
taro (cocoyam)
Scientific Name
Pythium species
AUTHORS Helen Tsatsia & Grahame Jackson
Photo 3 William Wigmore and Maja Poeschko, Ministry of Agriculture, Cook Islands.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.
This mini fact sheet is a part of the app Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds
The mobile application is available from the Google Play Store and Apple iTunes.




Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved.
 Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens & Weeds - Mini Fact Sheet Edition