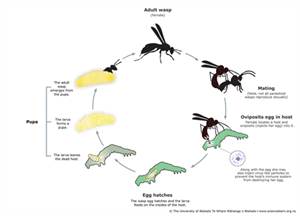
AUTHORS Graham Walker & Grahame Jackson
Information from Gardner-Gee et al. (2014) Effect of selected oils and insecticides on beneficial insect species: 2013/14 results. Report for Potatoes NZ. Plant & Food Research; and May et al. (2015) Minimizing Pesticide Risk to Bees in Fruit Crops. Extension Bulletin E3245, May 2015, Michigan University; and Ndakidemi B, et al. (2016) Impacts of Synthetic and Botanical Pesticides on Beneficial Insects. Agricultural Sciences: 7, 364-372; and Walsh B (2005) Impact of insecticides on natural enemies found in brassica vegetables. Poster, National Diamondback moth project team, Horticulture Australia Ltd.; and from University of California Statewide Integrated Pest Management Program. (http://ipm.ucanr.edu/GENERAL/pesticides.html). Diagram Science Learning Hub. Pokapū Akoranga Pūtaiao, University of Waikato.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project HORT/2016/185: Responding to emerging pest and disease threats to horticulture in the Pacific islands, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.