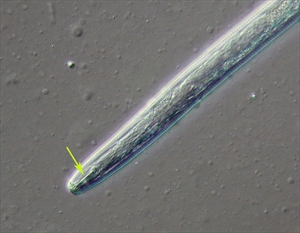
- Worldwide distribution. In tropics and sub-tropics. Root decay (red and black patches when split); weak bunches; and 'toppling'. Many crops and weeds. A important pest.
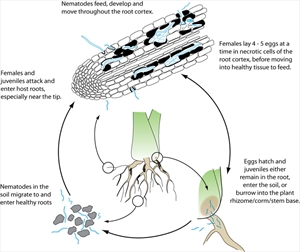
- Eggs are laid in roots or in soil nearby; larvae and adults tunnel through roots using a hollow spear to suck cell contents, and kill the roots.
- Spread is in ground water, and infested suckers.
- Cultural control: use non-host break crop (e.g., cassava, sweetpotato or a ground legume); before planting suckers: (i) remove soil and roots, inspect, cut out corm rots with knife wiped with bleach; (ii) treat with hot water - 53°C for 20 min.
- Chemical control: not recommended.
Pacific Pests, Pathogens and Weeds - Online edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides
Banana burrowing nematode (257)
Banana burrowing nematode, black head disease of banana
Radopholus similis
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Information (and Diagram) from Brooks FE (2014) Burrowing nematode. The Plant Health Instructor. (https://www.apsnet.org/edcenter/disandpath/nematode/pdlessons/Pages/Burrowingnematode.aspx); and Hauser S, Coyne D (2010) A hot bath cleans all: Boiling water treatment of banana and plantain. (https://www.ctc-n.org/sites/www.ctc-n.org/files/resources/4ea6bfcd-2658-4dac-bf31-03861661b3dc.pdf); and Vézina A, et al. (2020) Radopholus similis. ProMusa. (https://www.promusa.org/Radopholus+similis); and from Sikora NS, Crow W (2018) Featured Creatures, Entomology & Nematology. UF/IFAS, University of Florida. (http://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/NEMATODE/Radopholus_similis.htm). Photos 1-3 Fred Brooks, Plant and Environmental Protection Services, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.