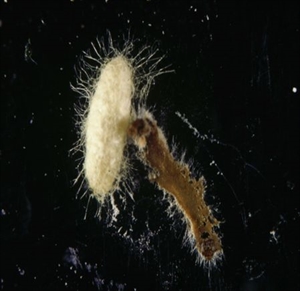
- Worldwide distribution. Common parasitising diamondback moth (DBM) in the hot lowland tropics and sub-tropics. Female lays 200 eggs, one in each young DBM caterpillars.
- Cotesia larvae eat DBM caterpillar from inside, emerges from the caterpillar and makes a cocoon on the brassica leaf. Look for white, oval pupa. The adult wasp (2-3.5 mm long) hatches after about 7 days and feeds on nectar.
- Cotesia cannot prevent damage by DBM alone. IPM programs avoid pyrethroids and organophosphates (these kill Cotesia and predators) and recommend use of Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis).
- Monitor and only use Bt when needed; rotate this with other insecticides to prevent resistance to Bt developing.
Pacific Pests, Pathogens and Weeds - Online edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides
Cotesia species (287)
Click/tap on images to enlarge
Summary
Common Name
Cotesia
Scientific Name
Cotesia vestalis; previously Cotesia plutellae. The wasp belongs to the family Braconidae.
AUTHORS Mike Furlong and Grahame Jackson
Information from Furlong MJ, et al. (2013) Diamondback moth ecology and management: problems, progress and prospects. Annual Review of Entomology 58:517-541. Photos 1-3 Mike Furlong, University of Queensland, Brisbane.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.