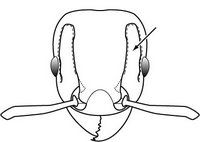
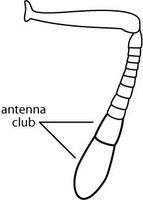
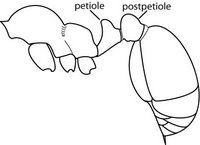
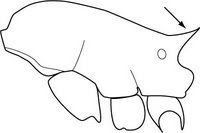
- Worldwide. A major pest; it forms super-colonies.
- Golden brown, 1.5 mm with painful sting. Nests under leaf litter, wood, in tree forks, with queens, workers, pupae and eggs. Eats many kinds of foods, and that is part of its success. A problem for workers in food gardens and plantations.
- Spreads in floating debris, in soil, and in the plant and log trades.
- Biosecurity: define risk, and have rapid response plan should an introduction occur.
- Chemical control: three types are used: (i) stomach poisons; (ii) growth regulators; (iii) neurotoxins. See IUCN/SSC website for details of eradication and management.
Pacific Pests, Pathogens and Weeds - Online edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides
Little fire ant (182)
Little fire ant, electric ant
Wasmannia auropunctata
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
1International Union for Conservation of Nature/Species Survival Commission. Information, photos (and Diagrams) Wasmannia auropunctata (PIAkey - identification guide to invasive ants of the Pacific islands. (http://itp.lucidcentral.org/id/ant/pia/index.html); and Electric ant. Wikipedia. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_ant); and Fasi J, et al. (2016) Subsistence farmers' management of infestations of the little fire ant in garden plots on Bauro, Makirta Province, Solomon Islands. Human Ecology 44: 765-774; and from (including Photos1-8) Walker, K. (2006) electric ant (Wasmannia auropunctata): PaDIL - http://www.padil.gov.au.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.