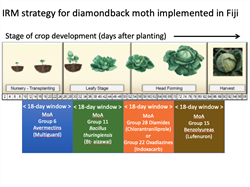
Insecticides can be grouped in different ways, but the most common way is how they kill insects. We call this their Mode of Action. Insecticides work in one of four known ways - how a small number work is not yet known.
-
Nerve and muscle: most insecticides target these, and they are usually fast acting
- Growth and development: the insecticides target the controls of growth and moulting, and are usually slow acting
- Respiration: the insecticides target mitochondria, the parts of cells that create energy, and are usually quite fast acting
- Midgut: the insecticides are specific toxins that target the gut, and they are quite slow acting
The Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC: www.irac-online.org) has divided these general modes of action further into 34 groups. Table 1 shows the groups to which the most frequently used classes of insecticides belong.
Table 1. Modes of action of classes of frequently used insecticides, with examples.
|
Mode of Action |
Group |
Class |
Examples |
|
Nerves (ACHE1 inhibition) |
1 |
Carbamates |
Aldicarb, Carbaryl, Methomyl |
|
1 |
Organophosphates |
Acephate, Dimethoate | |
|
Nerves (GABA Cl2 blocking) |
2 |
Organochlorines |
Endosulfan |
|
Nerves (Na channel, open) |
3 |
Pyrethroids, Pyrethrins |
Bifenthrin, Deltamethrin, Pyrethrum |
|
Nerves (nACHR3 binding) |
4 |
Neonicotinoids |
Acetamiprid, Imidacloprid |
|
4 |
Nicotine |
Nicotine | |
|
Nerves (nACHR alteration) |
5 |
Spinosyns |
Spinosad, Spinetoram |
|
Nerves (GluCL4 activation) |
6 |
Avermectins |
Abamectin, Emamectin benzoate |
|
Nerves (Na channel, close) |
22 |
Oxadiazines |
Indoxacarb |
|
Muscle (RR activation)5 |
28 |
Diamides |
Chlorantraniliprole, Flubendiamide |
|
Growth (disrupt moulting) |
7 |
JH6 analogues |
Methoprene |
|
Growth (chitin inhibition) |
15 |
Benzoylureas |
Lufenuron, Teflubenzuron |
|
Midgut (disruption/lysis) |
11 |
Bacillus thuringiensis |
Bt aizawai, Bt kurstaki |
|
Respiration (mitochondria) |
21 |
Rotenone |
Derris, Tephrosia |
1ACHE (Acetylcholine Esterase); 2 GABA Cl (Gaba-gated Chloride Channels); 3nAChR (Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor); 4GluCl (Glutamate Chloride channels); 5RR (ryanodine receptors); 6JH (juvenile hormone).