Sugarcane red rot
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides - Online edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides
Sugarcane red rot (221)
Glomerella tucumanensis; different strains are reported that vary in their ability to cause disease. The fungus is also known by its asexual stage, Colletotrichum falcatum. In Brasil, Colletotrichum siamense and Colletotrichum plurivorum are also the cause of red rot disease.
Asia, Africa, North, South and Central America, the Caribbean, Europe, Oceania. It is recorded from Australia, American Samoa, Cook Islands, Fiji, French Polynesia, Guam, Federated States of Micronesia, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu.
Sugarcane, other Saccharum species, maize and sorghum, and wild sorghum (Sorghum halepense).
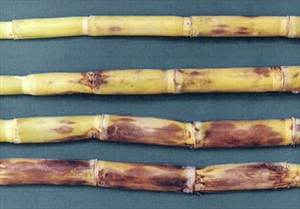
Stems show large red blotches on the outside (Photo 1), and internal red rots with white patches, when the stems are cut open (Photo 2). Cavities may be present which contain the cottony growth of the fungus. The leaves turn yellow, dry and die. As the rots develop, the stems are easily broken. Stems are infected through the nodes (where the leaf buds and roots develop) and through wounds.
On the leaves, small red oval spots occur on the midrib and upper surface of the leaf; these develop pale yellow to white centres, sometimes merging to cover the length of the leaf (Photo 3).
Spread of the fungus occurs in planting material, and this can be over both short and long distances. Spread also occurs in water, when spores produced on infected plants are splashed to those nearby, or in that used for irrigation. The fungus can survive for a few months in the soil, on plant debris and in sugarcane stems. Infection of the stems occurs through direct penetration of the nodes (buds, leaf scars or roots), from the fungus in the soil or in rain/irrigation water.
Cool, wet weather, heavy soils, and continuous planting of the same variety in the same land favour the disease. Drought also increases susceptibility.
The fungus attacks setts in the soil, causing them to rot as they sprout, and it also infects the standing crop causing plants to wilt and shrivel. In addition to the loss of plants, there is a reduction of sucrose content in those that are affected by rots. Severe losses in yield of cane and, consequently, sucrose have been reported from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Thailand, and it is likely that similar losses occur elsewhere.
Look for red blotches on the stems and elongated spots in the midribs on the top surface of leaves. Look for white spots or blotches in the pith which are usually elongated at right angles to the long axis of the stem; these are diagnostic for this disease.
CULTURAL CONTROL
Before planting:
- Use healthy setts; take planting material from fields where the disease has not been seen.
- Plant when either wet or dry times will be avoided.
- If growers have only a small number of setts, treat with hot water at 50°C for 2 hours; obviously, this is not an appropriate method for large amounts of planting material.
- Avoid heavy soils which have a tendency to become waterlogged. Red rot is reported to be worse where poor drainage and infection by Pythium (an oomycete) occur together.
After harvest:
- Collect the remains of the crop and burn it.
- Do not ratoon diseased crops, otherwise the fungus may increase to an epidemic.
- Plough the field several times to expose the fungus to sunlight.
- Do not plant one crop of sugarcane after another in the same land; use a rotation of at least 2-years.
RESISTANT VARIETIES
There are varieties resistant to this disease; check those available in your area. There are, however, a number of strains of this fungus.
CHEMICAL CONTROL
This is not a method that can be used to control this disease economically.
AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
Information (and Photos 1&2) CABI (2014) Glomerella tucumanensis (red rot of sugarcane) Crop Protection Compendium. (https://www.cabi.org/cpc/datasheet/25361); and from Marins EFC, et al. (2022) Colletotrichum species associated with sugarcane red rot disease. Fungal Biology 126(4): 290-299. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35314060/). Photo 3 Kohler F, et al. (1997) Diseases of cultivated crops in Pacific Island countries. South Pacific Commission. Pirie Printers Pty Limited, Canberra, Australia.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.