- Narrow distribution. Common in Papua New Guinea. It spread to Solomon Islands in the 1980s. On bele (aibeka, slippery cabbage). An important pest.
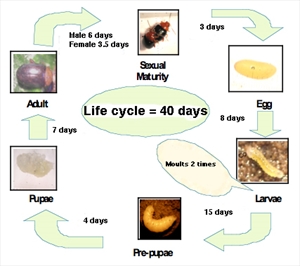
- Eggs laid in soil near the stem; larvae feed on small roots, then pupate; adults (4 mm long) feed on leaves.
- Leaves are ruined as a food by the presence of the many holes.
- Cultural control: plant far from infested crops; plant in clover, under shade, or in the wet season; handpick; cultivate around stem to expose eggs; use thick grass mulches; put horticultural glue bands (e.g., Tanglefoot) around stems.
- Chemical control: spray with wood ash (ash + lime in water); alternatively, PDPs: neem, derris and pyrethrum, or spinosad; or synthetic pyrethroids, but likely to kill natural enemies.