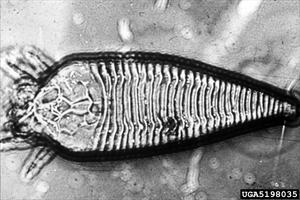
- Worldwide distribution. Citrus species. An important microscopic mite.
- Rind slightly rough, silvery (grapefruit and lemons), reddish or black (oranges). Small fruit, which stores poorly. Foliage turns bronze with heavy infestations. Worse on fruit on outside of tree.
- Eggs in pits in leaves or stems; nymphs and adults similar: yellowish, wedge-shaped; adults 0.15 mm long.
- Spread in rain splash, and over greater distances on wind currents, on birds, insects, machinery, clothing, or in the plant trade.
- Natural enemies: predatory mites (Amblyseius).
- Cultural control: none.
- Chemical control: use pesticides if damage is severe - use lime sulphur or wettable sulphur, leaving 30 days if also spraying oils (READ INSTRUCTIONS); alternatively, spot-spray with soap solution, horticultural or white oils (see Fact Sheet no. 56); or use abamectin. Avoid malathion and synthetic pyrethroids; they will kill predatory mites.