- Worldwide distribution. In the tropics. The fungus has a wide host range, attacking native and exotic forest trees, plantation crops, including cocoa (and shade trees), oil palm, rubber, coffee. Attacks breadfruit (Pingelap disease). An important disease.
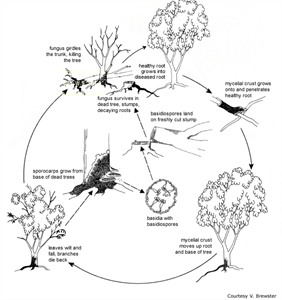
- Spores of the fungus infect tree stumps as land is cleared. The fungus travels along the roots to healthy trees, growing up to 1 m on the trunk as a thick brown crust, causing death. Brackets form on the old tree stumps 3-4 years after infection.
- Cultural control: survey plantations 6-monthly for brackets on stumps, and crusts on trunks; if seen, remove with all roots over 2.5 cm diameter.
- Chemical control: none recommended.
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides - Online edition
Pacific Pests, Pathogens, Weeds & Pesticides
Cocoa brown root rot (003)
Brown root rot
Phellinus noxius
AUTHORS Helen Tsatsia & Grahame Jackson
Information from Phellinus noxius root rot (Undated). Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation (Queensland Government). (https://www.daf.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/51211/phellinus_noxius_web.pdf); and CABI (2013) Phellinus noxius (brown tea root disease). Invasive Species Compendium.(https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/40154); and from (including Diagram) APSnet Education Center. Brown root rot. The American Phytopathological Society. (https://www.apsnet.org/edcenter/disandpath/fungalbasidio/pdlessons/Pages/BrownRootRot.aspx).
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.