AUTHOR: Mike Furlong
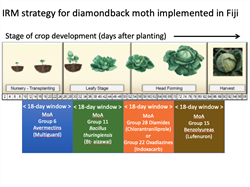
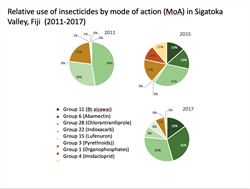
Information from IRAC: www.irac-online.org; and from Atumurirava F, et al. (2021). Development, implementation and monitoring of an insecticide resistance management strategy for diamondback moth in the South Pacific. VIII International Conference on Management of the Diamondback Moth and Other Crucifer Insect Pests, Shanhua, Tainan, Taiwan, 4-8 March 2019. Shanhua, Tainan, Taiwan: World Vegetable Center.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project HORT/2016/185: Responding to emerging pest and disease threats to horticulture in the Pacific islands, implemented by the University of Queensland, in association with the Pacific Community.