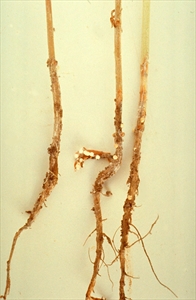
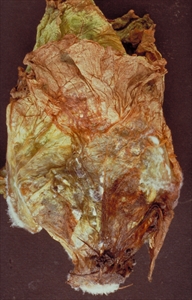
- Worldwide distribution. On many vegetables, fruit and field crops. Important disease in sub-tropical countries.
- Cottony growth causes rots of roots, stems, leaves and fruits; also, damping–off. Black, survival bodies ('sclerotia') form, later producing a toadstool and liberating spores infecting dying leaves and flowers.
- Cultural countries: wide spacing; trellis; prune lower leaves/branches; crop rotation; soil sterilisation; add manures; mulch, do not harvest and pack in wet weather; plough in trash or collect and burn.
- Chemical control: seed treatments: thiram or captan; in the field: benzimidazole, strolbilurin or triazole fungicides.