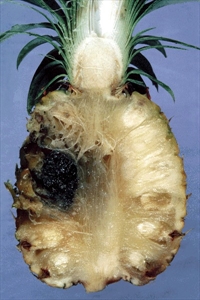
- Worldwide distribution. On pineapple, cocoa (pod rot), coconut (stem bleeding), banana and plantain (black end or fruit rot), maize, mango, potato, sugarcane (pineapple disease, see Fact Sheet no. 218), sweetpotato (see Fact Sheet no. 232) and taro. An important disease.
- A fungus causing, (i) long, white papery spots on leaves which rub together; (ii) black, soft watery rots under brittle skin on fruit damaged at harvest when wet; (iii) soft grey rots at base of planting materials when detached wet, and stored in heaps.
- Cultural control: (i) fruit - handle carefully; reject sunburnt fruit; keep packing shed clean; (ii) planting material – store in single layer, inverted with butts exposed to sun; (iii) planting - improve drainage and avoid planting when wet.
-
Chemical control: dip fruit in prochloraz, and planting material in propiconazole.