AUTHOR Grahame Jackson
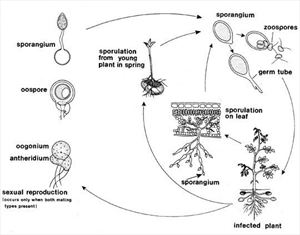
Information from CABI (2015) Phytophthora infestans (Phytophthora blight) Crop Protection Compendium. (https://www.cabi.org/cpc/datasheet/40970); and information (and Diagram) from Schumann G, D’Arcy CJ (2000) Late blight of potato and tomato. The Plant Health Instructor. DOI: 10.1094/PHI-I-2000-0724-01. Updated 2005. Photo 2 Howard F. Schwartz, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org. Photo 3 Agriculture Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture.
Produced with support from the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research under project PC/2010/090: Strengthening integrated crop management research in the Pacific Islands in support of sustainable intensification of high-value crop production, implemented by the University of Queensland and the Secretariat of the Pacific Community.