- Restricted. Asia, Oceania. In American Samoa, Australia, Fiji, French Polynesia, Guam, New Caledonia, Northern Mariana Islands, Papua New Guinea. Samoa, Solomon Islands.
- In Asia, minor rice pest; in Fiji, major pest on high-yielding varieties beginning in 1970s. Also on maize, wild grasses.
- Larvae eat inside tunnels of folded or bound leaves, creating long white stripes. Fields appear grey.
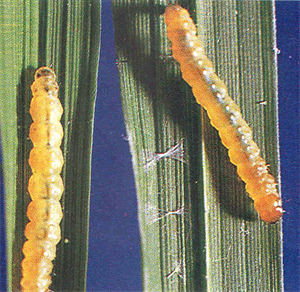
- Eggs laid singly or in small groups, overlapping in rows, often on tallest plants. Larvae yellowish-green with pale-brown heads, up to 11 mm, feed together initially then disperse. Pupate on leaves. Adults pale-yellow wings with grey-brown borders, wingspan 13 mm, with 3-4 bands.
- Natural enemies: many egg and larval parasitoids and predators. In Fiji, Trichogramma and Trathala flavo-orbitalis destroy >40% of larvae.
- Biosecurity: introduction possible on produce contaminated with infested stems of host plants.
- Cultural control: increase plant spacing; fallow land or rotate crops; do not over-fertilise; remove weeds within and around crops; do not ratoon crops; flood fields after harvest or plough in straw and stubble; resistant varieties (new, high-yielding varieties susceptible).
- Chemical control: use neem, abamectin, or spinosad. Avoid broad-spectrum products.