- Worldwide distribution. On watermelon, cantaloupe melon and cucumber (see Fact Sheet no. 201). An important disease.
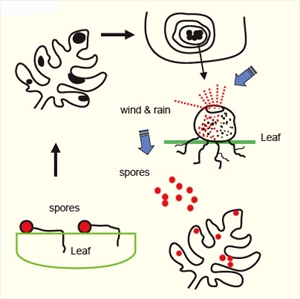
- Spots on leaves grow rapidly, leaves blacken shrivel and die. Spots on vine leak a gummy (sticky) liquid.
- Spread as spores from black sacs on the leaf spots in wind and rain.
- Cultural control: site nursery away from production areas; pasteurised soil or soilless mixes; check each seedling for spots, and discard if seen; 3-year rotation; do not plant next to diseased watermelon crops; collect and destroy trash after harvest.
- Chemical control: coppers, mancozeb, or chlorothalonil every 7-10 days, depending on weather.