- Worldwide distribution; present in Australia and New Zealand. On more than 250 plants in 65 families; these include: soft fruit (plums, peaches, strawberries, grapes); flowers (Gladiolus, Impatiens, Gerbera, Chrysanthemum, poinsettia); vegetables (cucumber, tomato, capsicum, cabbages, beans), and wild flowers. An important pest.
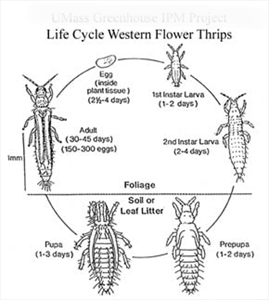
- Eggs laid in flowers or leaves; nymphs and adults cause distortions, spots and silvering, and spread viruses (e.g., Tomato spotted wilt virus).
- Spread by short flights, and by the plant trade.
- Cultural control: check seedlings in nurseries – if necessary, use thrips-grade screen; 10 m grass strips around nurseries; avoid planting new crops near old; weed; apply adequate nutrition and irrigation; use yellow or blue sticky traps to monitor thrips; rogue plants with virus; collect and burn trash after harvest; crop rotation.
- Chemical control: soap, white or horticultural oils, neem, spinosad, entomopathogenic fungi (Beauveria bassiana) and nematodes (Heterorhabditis and Steinernema); note, thrips has resistance to many synthetic pesticides, and these are best avoided.