- Worldwide distribution. On yam, banana, and many other crops and weeds. Note, the burrowing nematode, Radopholus similis, causes a similar disease on banana (see Fact Sheet no. 257). An important disease.
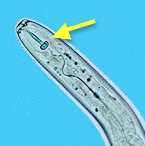
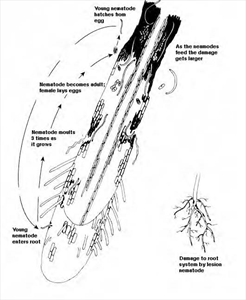
- Eggs are laid in roots or nearby in soil; young larvae, and adults, tunnel through roots and tubers using a hollow spear to suck cell contents. Roots are killed.
- Spread is in ground water, and infested tubers and setts used for planting.
- Cultural control: non-host break crop (e.g., cassava, sweetpotato, ground legumes – Mucuna or Pueraria; discard sets with rot, or cut out with knives wiped in bleach; alternatively, treat yam setts in hot water (51°C for 10 minutes) or, for banana sets, (53°C for 20 mins.); avoid storing tubers with rots, and if seen remove; 3-year crop rotation.
- Chemical control: none recommended.