Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants - Online edition
Ochrosia elliptica Labill.



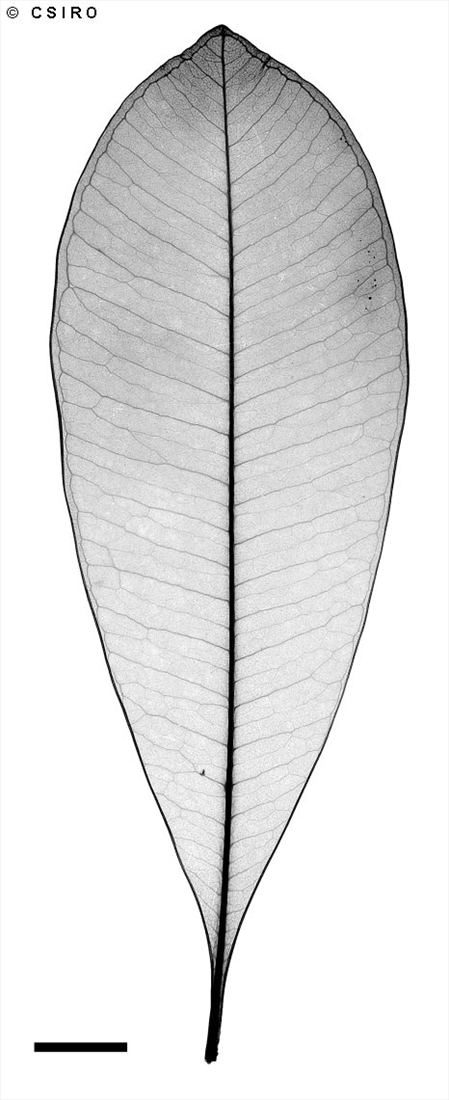

Labillardiere, J.J.H. de (1825) Sertum Austro-Caledonicum : 25. Type: New Caledonia, J. J. H. de Labillarddiere s. n.; holo: P.
Bloodhorn; Scarlet Wedge-apple; Ochrosia
Occasionally grows into a small tree but usually flowers and fruits as a shrub about 3 m tall.
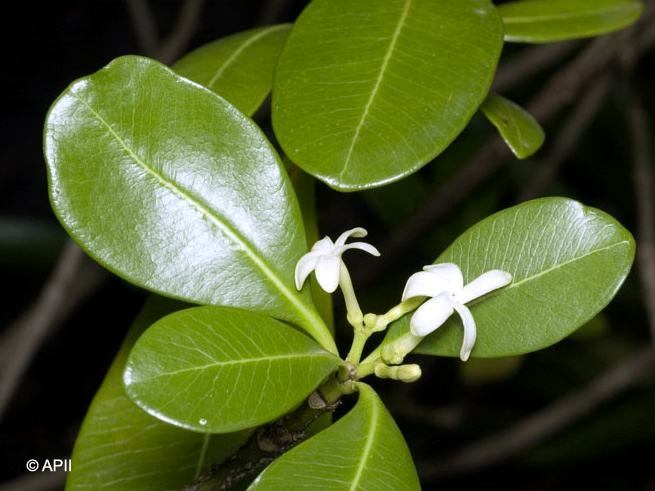
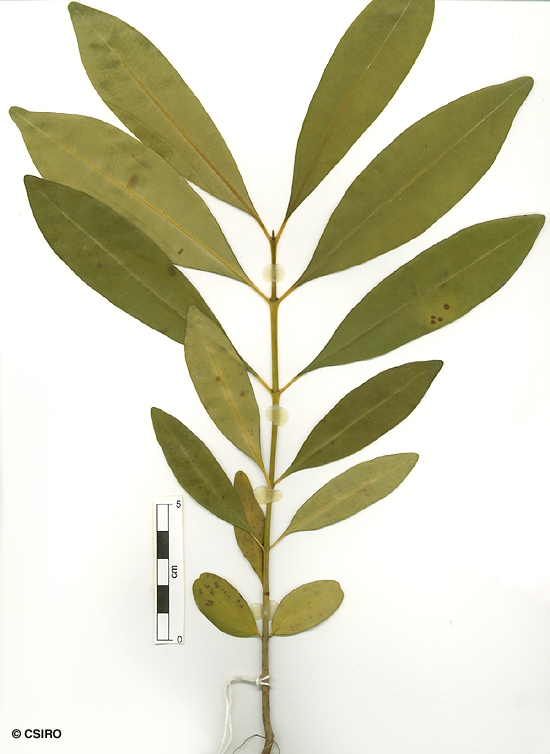
Twigs and petioles produce a milky exudate. Intramarginal vein (or two intramarginal veins) quite distinct particularly on the underside of the leaf blade, intramarginal vein 1 mm or more from the margin. Leaves usually in whorls of three or four. Numerous brown processes (glands?) up to 1 mm long wedged between the petiole and the twig. Leaf blades about 11-17 x 3.5-7 cm, petioles about 0.5-1.1 cm long, channelled on the upper surface. Lateral veins about 20-25 on each side of the midrib.
Flowers about 12-14 mm diam. Calyx lobes about 2 mm long. Corolla tube about 12-13 mm long, lobes glabrous, about 9-19 mm long. Anthers longer than the filaments, inserted in the corolla tube about 2 mm from the apex, gradually tapering to a point at the apex. Anthers included in the corolla tube at anthesis. Ovules attached to a comparatively large marginal placenta. Styles two, joined at least towards the apex. Stigma globular with two small lobes at the apex.
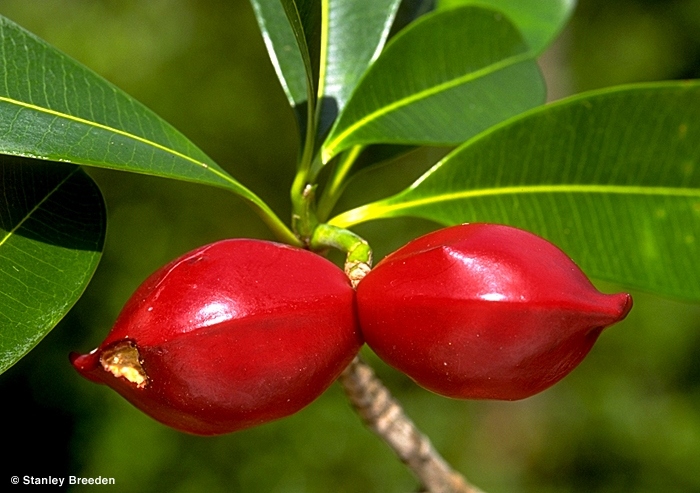
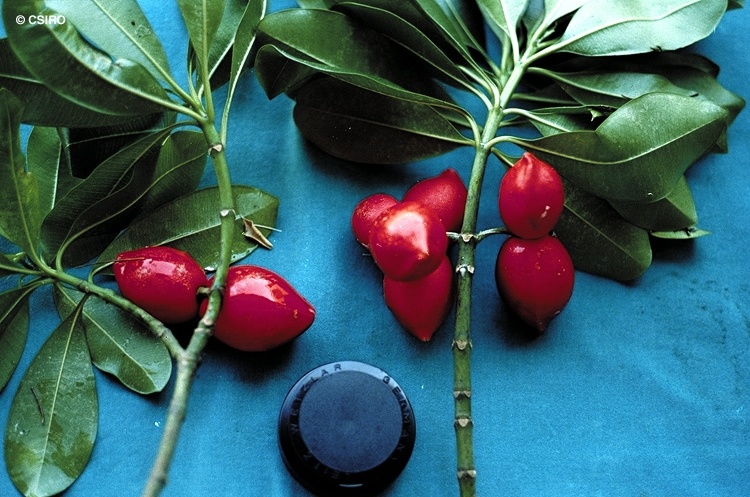
Fruits produce a milky exudate. Fruits glossy red, about 5-6 x 2-3 cm, with large structures (within the endocarp) which at first sight look like seeds but are not. Their function is not obvious but it may have something to do with buoyancy. Cotyledons much broader than the radicle.
Cotyledons ovate to elliptic, about 33-36 x 18-20 mm, petiole short. First pair of leaves narrowly elliptic or narrowly ovate, about 60 x 17 mm, margins entire. At the tenth leaf stage: leaf blade elliptic or obovate, apex obtuse or acute, base attenuate, glabrous. Stems and leaves produce a milky exudate. Seed germination time 270 to 522 days.
Occurs in NEQ, CEQ and southwards to south-eastern Queensland. Altitudinal range small, usually close to sea level. Grows in beach forest or on the landward side of mangroves. Occasionally cultivated and survives quite happily at an altitude of 750 m on the Atherton Tableland. Also occurs in the Pacific islands.
Sap poisonous. Austin, D. F. 1998. Poisonous Plants of Southern Florida.
Leaf and stem material of this species was active against some tumors. Collins et al. (1990).
This plant was used in colonial medicine, bark used to treat malaria, but contains no quinine. Cribb (1981).





