Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants - Online edition
Abrus precatorius L.





Linnaeus, C. von (1767) Systema Naturae 2: 472. Type: Tropical regions.
Precatory Bean; Pun-dir Pun-dir; Crab's-Eye Creeper; Giddee-Giddee; Gidee Gidee; Crab's Eyes; Crab's Eye Vine; Indian Liquorice; Do-anjn-jin; Jequirity Bean; Crab's Eye; Rosary Pea; Vine, Crab's Eye; Jequirity
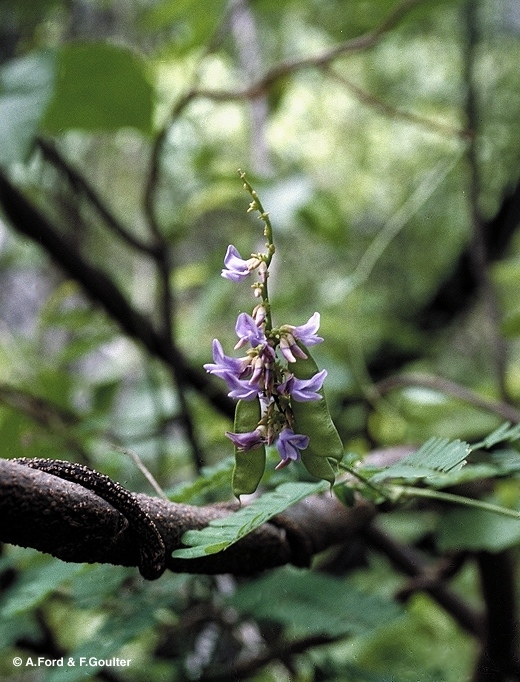
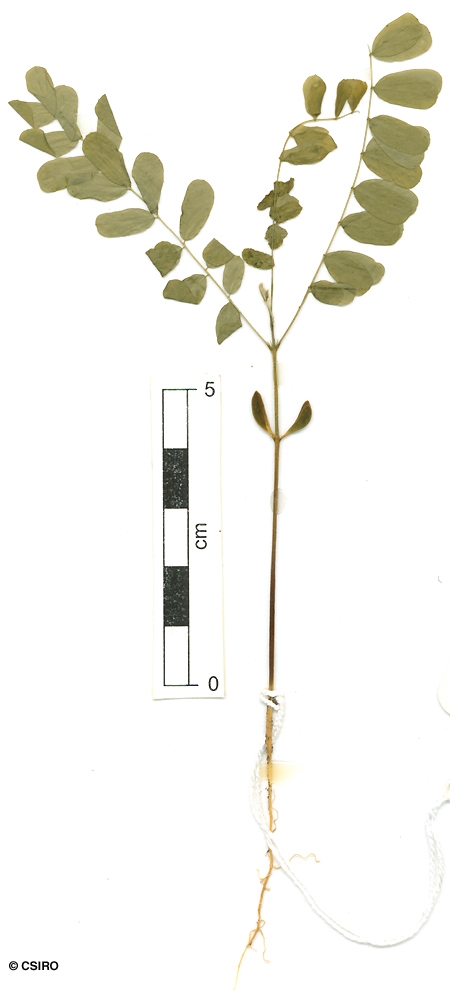
A slender vine which grows during the wet season and dies back in the dry. Stem diameter not exceeding 2 cm.
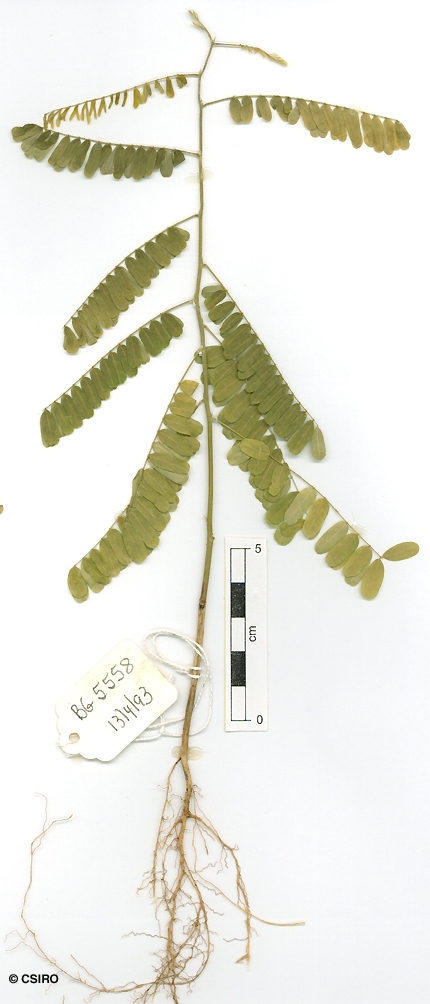
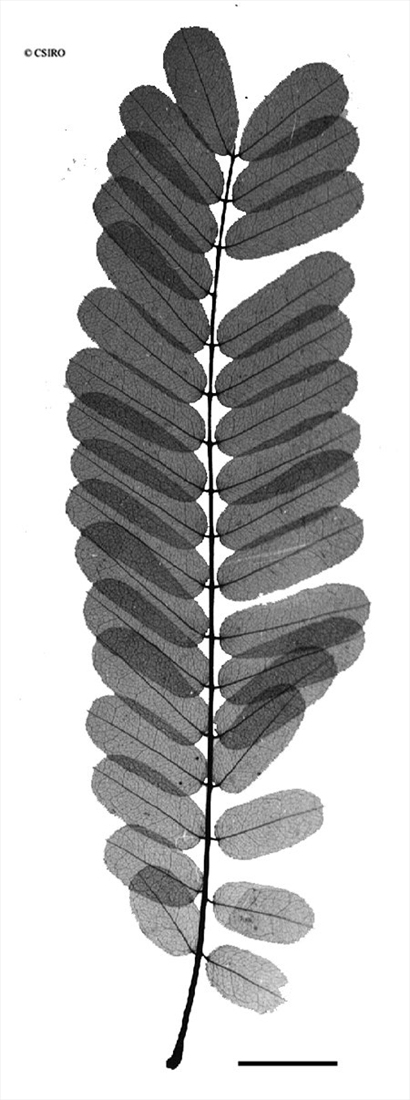
Stipules narrowly triangular, about 3-4 mm long. Leaflets 8-36 per compound leaf, each leaflet blade about 16-25 x 6-8 mm, underside sparsely clothed in prostrate hairs, leaflet stalks less than 1 mm long. Compound leaf rhachis clothed in pale prostrate hairs. Rhachis and petiole deeply grooved on the upper surface. Lateral veins and reticulate veins equally well defined. Stipels usually visible on the upper surface of the compound leaf rhachis at the point of attachment of the pairs of leaflets.
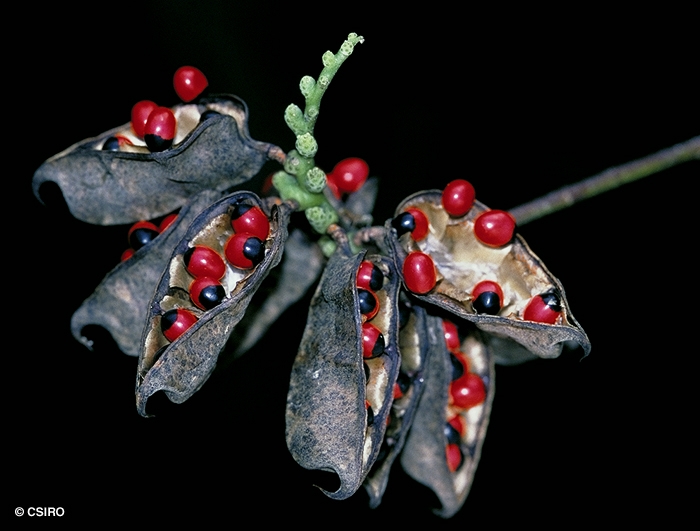
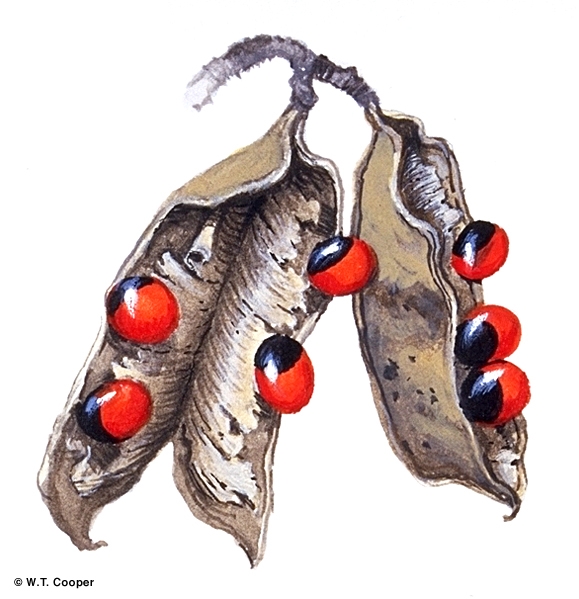
Fruits about 25-50 x 15 mm, opening along one or two sutures to expose 3-7 seeds. Seeds very poisonous. Seeds about 5-7 x4- 5 mm, shiny, upper half of the testa red, basal half black. Cotyledons about 5-6 mm long, radicle about 1-1.5 mm long.
Cotyledons thick and fleshy, about 9-10 x 3-4 mm, sessile or almost sessile. Cotyledonary stipules about 1.5 mm long. First pair of true leaves opposite, pinnate with 16-18 leaflets per leaf. Stipules about 1-2 mm long. At the tenth leaf stage: leaf pinnate with about 22-30 leaflets. Stipules about 1.5-2 mm long. Stipels present. Leaflet blades about 10 x 3-3.5 mm. Seed germination time 11 to 124 days.
Occurs in WA, NT, CYP, NEQ, CEQ and southwards as far as south-eastern Queensland and perhaps north-eastern New South Wales. Altitudinal range in northern Australia from near sea level to 500 m. Frequently grows in beach forest, also found in vine thicket and monsoon forest. Also occurs in Africa, Asia, Malesia and the Pacific islands.
The seeds of this species contain albrin one of the most powerful poisons known. There is more than enough albrin in one seed to kill a man but if the seed coat is unbroken the toxin is not released. Everist (1974).
This species has medicinal properties and is also very poisonous. Action: anodyne, aphrodisiac, central nervous system sedative, contraceptive, emetic, emollient, expectorant, febrifuge, haemostat, laxative, pectoral, purgative, refrigerant, sedative, urogenital, venereal, vermifuge.
The attractive seeds are extremely poisonous; they have been used criminally for poisoning in India. Roots and leaves of this species are regarded as medicinal in a number of countries. Cribb (1981).





