Euclid - Online edition
Corymbia bella
Corymbia | Blakearia
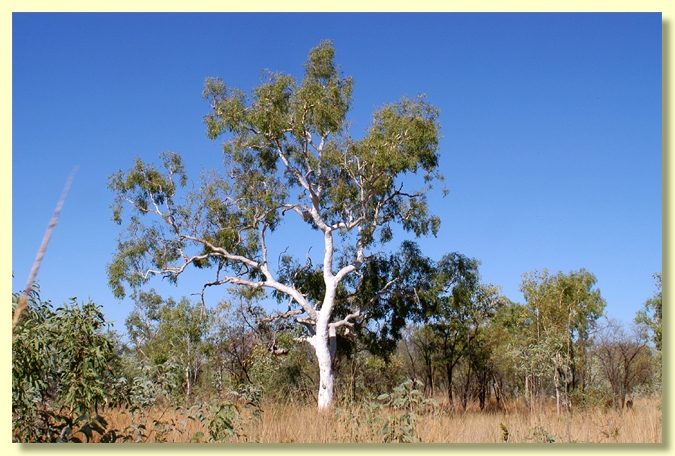
Tree to 20 m tall. Forming a lignotuber.
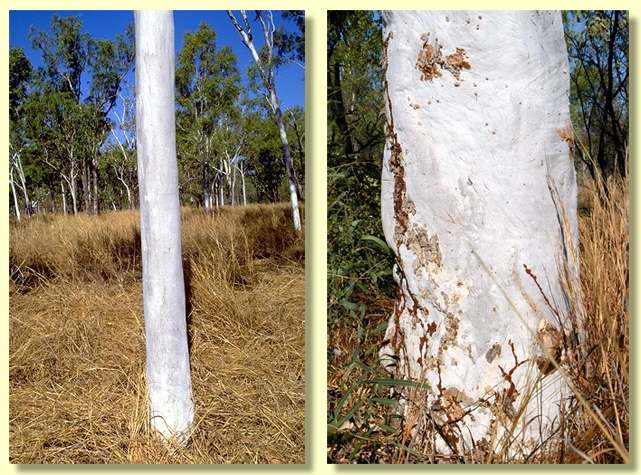
Bark smooth throughout, powdery, white to creamy white or pale grey; rarely with scant thin rough bark at the very base of the trunk.
Branchlets lack oil glands in the pith; non-glaucous, smooth.
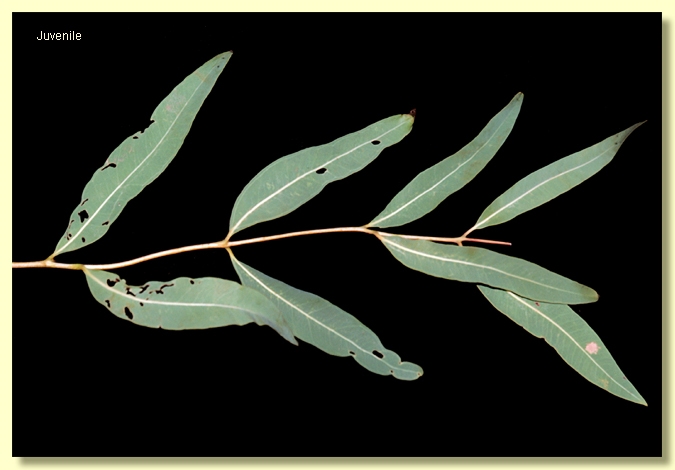
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stems rounded in cross-section, smooth; juvenile leaves petiolate, opposite or tending to sub-opposite, smaller elliptic at first soon becoming longer and lanceolate up stem, 6.5–11(19) cm long, 1.7–3 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, green, dull, glabrous.
Adult leaves alternate, occasionally a pair opposite, petioles 0.5–2.1 cm long; blade lanceolate to narrowly so or slightly falcate, 7–23 cm long, 0.6–2.5 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, margin entire or coarsely indented, apex pointed, undulate, concolorous, green to slightly grey-green, dull or slightly glossy, usually with side-veins at greater than 45° to midrib, reticulation dense to very dense, intramarginal vein present, oil glands obscure.
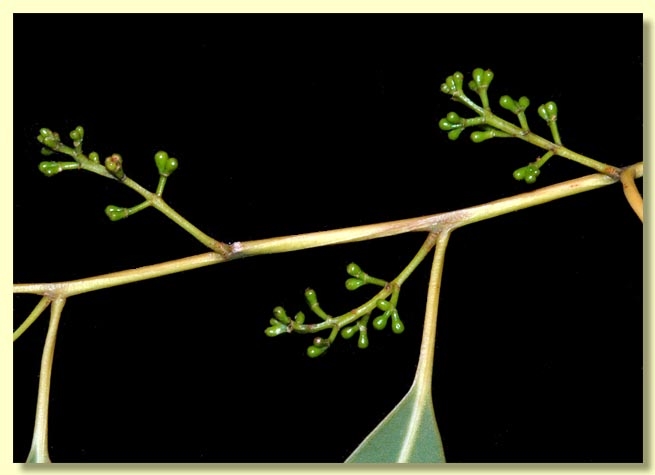
Inflorescence axillary compound or rarely terminal compound, with an expanded rhachis with 2 to 4 internodes, the basal internode 0.5–1 cm long and subsequent internodes each up to ca 0.2–0.5 cm long, peduncles variable within an inflorescence, 0.1–0.9 cm long, buds usually 3 per umbel (rarely 7), on pedicels 0.1–0.5 cm long. Mature buds pyriform (0.5–0.7 cm long, 0.4–0.5 cm wide), smooth, scar present (outer operculum shed early), operculum shallowly rounded and sometimes apiculate, stamens inflexed, all fertile, anthers ± cuboid, dorsifixed, versatile, dehiscing by longitudinal slits, style as long as or shorter than the floral cavity, straight, stigma blunt, locules 3, the ovules irregularly arranged on the placentae. Flowers creamy white, perfumed.
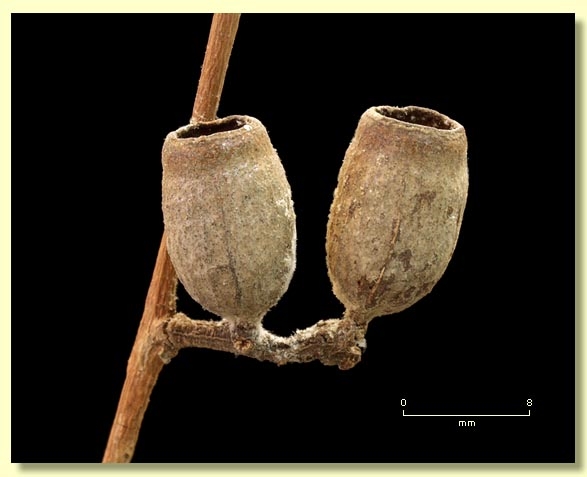
Fruit pedicellate (pedicels 0.1–0.6 cm long), cupular to barrel-shaped or urceolate, 0.8–1.1 cm long, 0.6–1.1 cm wide, thin-walled, disc descending vertically, valves 3, enclosed.
Seeds brown, 3–7 mm long, saucer-shaped, smooth, hilum ventral.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): not grown.
Flowering has been recorded in January, September, October, November and December.
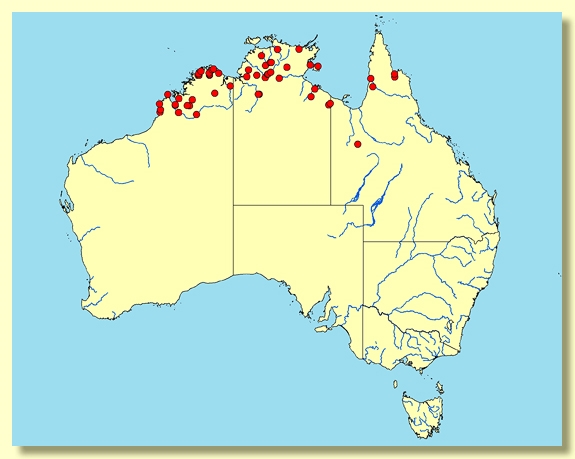
A ghost gum tree from monsoonal northern Australia, common from Broome to the Mitchell Plateau, Kununurra and Halls Creek in Western Australia, through the Top End of the Northern Territory from Top Springs, Dorisvale, Pine Creek, Mainoru, north to Port Keats, Darwin, Annaburroo, Oenpelli and Yirrkala, extending around the Gulf of Carpentaria to Bing Bong and into northern Queensland from Doomadgee east to Cloncurry, Croydon and the south-western part of Cape York Peninsula at least as far as the lower Mitchell River. Corymbia bella prefers floodplains and other low-lying seasonally wet sites where it is a component of woodlands, occurring on or near creek levees or edges of Melaleuca swamps and on low sites on plains as part of open savannah woodland.
C. bella is a smooth-barked tree with a green crown of alternate, petiolate, green, glabrous, often dull leaves. The flowers occur in axils of the current leaf crop or just below. The white flowers are borne in an expanded compound inflorescence with obvious internodes between successive clusters of flowers. The fruits are thin-walled and the seeds saucer-shaped and are shed immediately the fruit are mature, like all ghost gum species.
When in bud or when flowering C. bella is easily distinguished from all other ghost gums within its natural range, except for C. arafurica, by the expanded inflorescence structure with several clearly visible internodes. C. bella is distinguished from C. arafurica by the much smaller juvenile leaves (always wider than 7 cm in C. arafurica). Of the other smooth-barked ghost gums C. grandifolia has larger, glossy green crown leaves and larger buds and fruit with much longer pedicels, while the Kimberley endemic C. torta has highly undulate narrowly lanceolate adult leaves and lives on rocky rises. C. bella is closely related to C. tessellaris of eastern Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales, which differs in having a stocking of prominently and clearly tessellated rough bark on the lower trunk but otherwise is very similar.
C. bella was long regarded as part of a very widespread species with very varied morphology, Eucalyptus papuana, a name to which any narrow-leaved, smooth-barked ghost gum seemed to have been referred. In EUCLID we restrict Corymbia papuana to Papua New Guinea and the northern tip of Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, and recognize C. bella and C. arafurica as being related to but distinct from it.
MORE ABOUT CORYMBIA
MORE ABOUT GHOST GUMS
Corymbia bella: Latin bellus, beautiful, referring to the tree as a whole.