Euclid - Online edition
Eucalyptus badjensis
Eucalyptus | Symphyomyrtus | Maidenaria | Euryotae | Compactae | Ambitae
T: 3 miles [c. 5 km] S of Big Badja Mtn, NSW, Jan. 1924, W.A.W. de Beuzeville s.n.; holo: NSW.
Tree to 45 m tall. Forming a lignotuber.
Bark rough on lower trunk only, compacted, hard, blackish or grey, upper trunk and branches smooth grey, green, cream, brown or white, often with ribbons of decorticated bark in the upper branches.
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stem rounded or square in cross section, sometimes warty; juvenile leaves opposite, sessile, usually amplexicaul, for many pairs, lanceolate, 3.5–8 cm long, 0.8–2 cm wide, green.
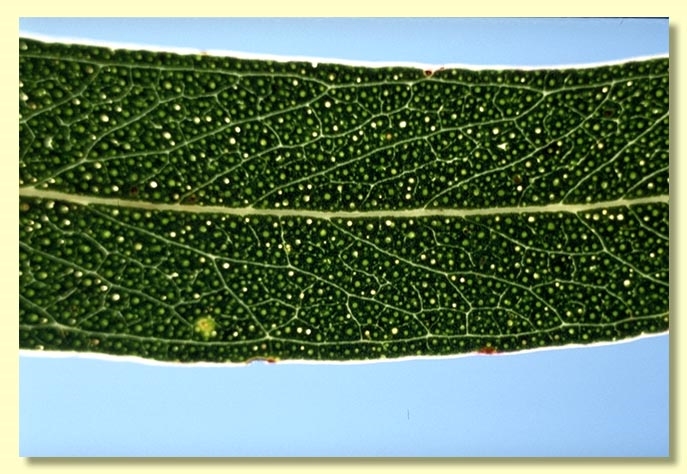
Adult leaves alternate, petiole 0.6–1.4 cm long; blade narrowly lanceolate to linear or falcate, 8.5–20 cm long, 1–2 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, concolorous, dull, green, side-veins at an acute or wider angle to midrib, sparsely to moderately reticulate, intramarginal vein parallel to and just within margin, oil glands mostly island.
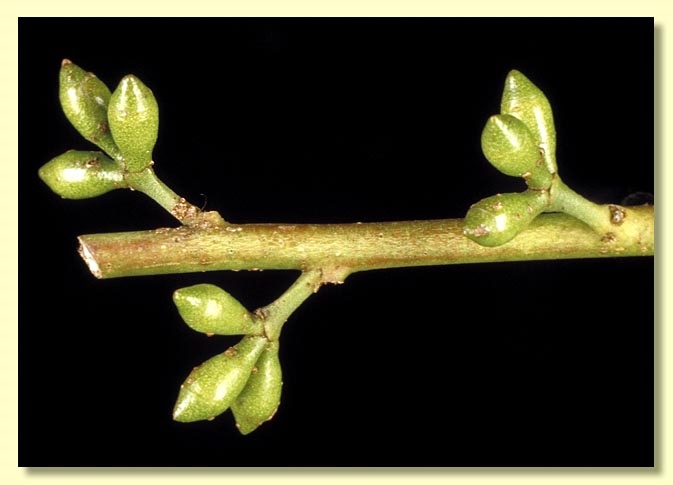
Inflorescence axillary unbranched, peduncles 0.3–0.4 cm long, buds 3 per umbel, sessile or on pedicels to 0.2 cm long. Mature buds ovoid, 0.4–0.5 cm long, 0.3–0.4 cm wide, green to yellow, smooth, scar present, operculum conical, stamens inflexed, anthers cuboid to oblong, versatile, dorsifixed, dehiscing by longitudinal slits (non-confluent), style long, locules 3 or 4, the placentae each with 4 vertical ovule rows. Flowers white.
Fruit sessile or on pedicels to 0.2 cm long, obconical or campanulate, 0.3–0.5 cm long, 0.4–0.6 cm wide, disc raised, valves 3 or 4, strongly exserted.
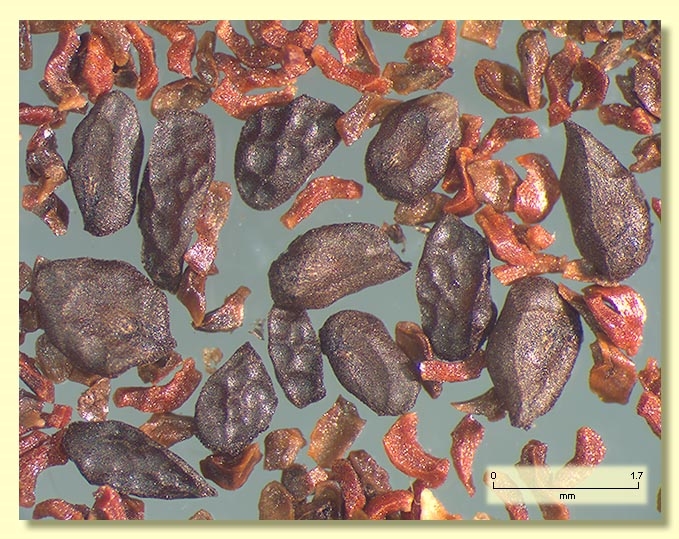
Seeds black, brown or grey, 1.6–2 mm long, ovoid or flattened-ovoid or pointed at one end, lacunose, dorsal surface smooth or shallowly reticulate, hilum ventral.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons bilobed to oblong; stems square to rounded in cross-section, warty; leaves sessile and opposite for at least 23 nodes, lanceolate, 3.5–6 cm long, 0.8–2.2 cm wide, stem-clasping, green.
Flowering has been recorded in January.
Eucalyptus badjensis is becoming an important plantation species for timber and fibre production.
A small to tall tree, restricted to the eastern side of the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, from Big Badja south to Cathcart.
Eucalyptus badjensis is distinguished by the rough, compacted basal bark, the small narrow adult leaves, the numerous pairs of green, opposite sessile lanceolate juvenile leaves, the buds in threes and the small obconical to campanulate fruit. The habit, bark and juvenile leaves resemble those of the unrelated E. elata , which has many buds per inflorescence, almost globular fruit and strong peppermint-scented leaves; and E. smithii, which has 7 buds per inflorescence and almost globular fruit including the strongly ascending disc.
E badjensis belongs in Eucalyptus subgenus Symphyomyrtus section Maidenaria, a large group of species more or less restricted to south-eastern Australia, characterised by bilobed cotyledons, simple axillary inflorescences, buds with two opercula, stamens with versatile anthers and flattened seeds with a ventral hilum. Within section Maidenaria, E. badjensis and E. smithii form series Compactae distinguished by the character of the hard basal bark and juvenile leaves.