Euclid - Online edition
Eucalyptus dives
Eucalyptus | Eucalyptus | Aromatica | Radiatae
T: N of Bathurst, NSW, Dec. 1822, A.Cunningham 181; iso: BM, K, MEL.
E. amygdalina var. latifolia H.Deane & Maiden, Proc, Linn. Soc. New South Wales 20: 609 (1896).
T: not designated.
Bark rough to the large branches, finely fibrous (peppermint-type), grey to grey-brown; smooth bark grey.
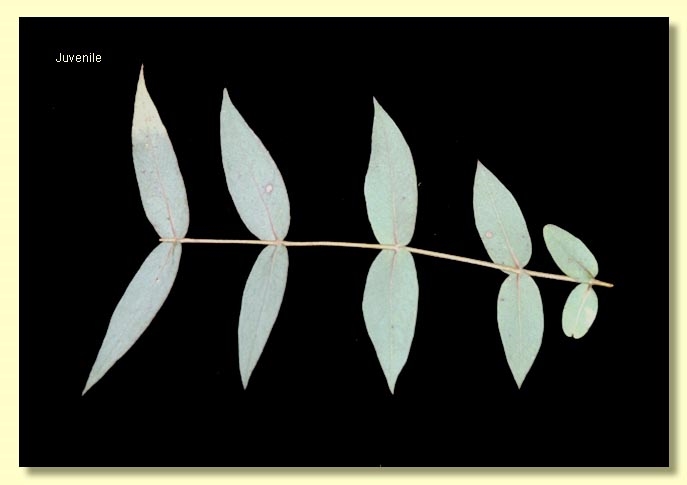
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stem rounded in cross-section, often glaucous; juvenile leaves opposite for many pairs, rarely connate, sessile, ovate to cordate to broadly falcate, 6–14 cm long, 2–7 cm wide, blue-green to blue-grey or glaucous.
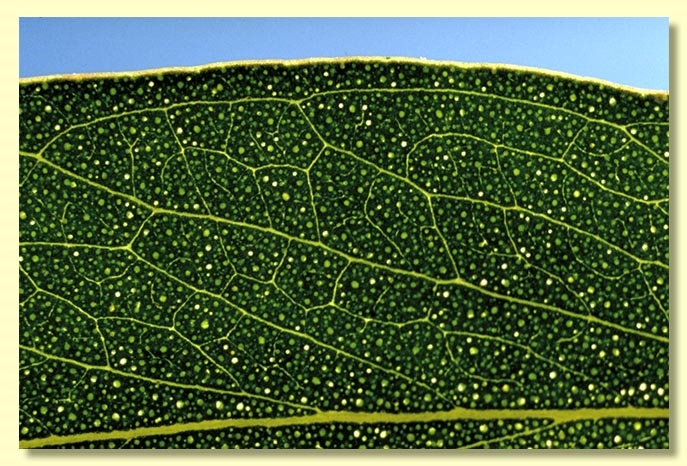
Adult leaves alternate, petiole 0.5–3.3 cm long; blade broadly lanceolate to lanceolate or falcate, 7–15 cm long, 1.4–4.2 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, concolorous, slightly glossy or dull, green, side-veins acute, sparsely to moderately reticulate, intramarginal vein parallel to and well removed from margin, oil glands island.
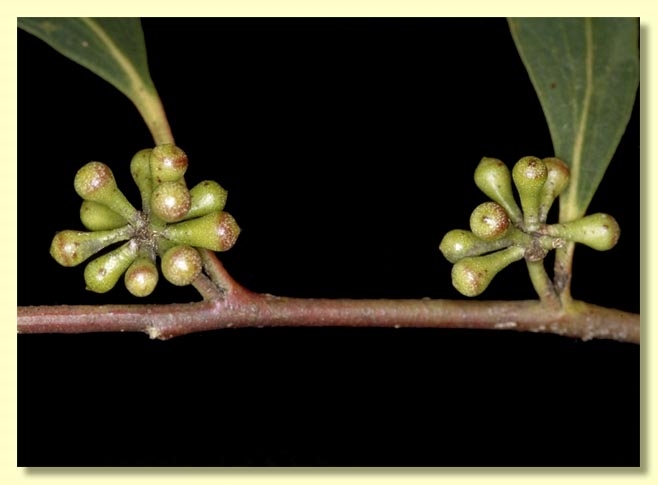
Inflorescence axillary unbranched, rarely paired in the axils, peduncles 0.3–1.5 cm long, buds 11 to many per umbel, pedicels 0.2–0.7 cm long. Mature buds obovoid to clavate, 0.3–0.6 cm long, 0.2–0.4 cm wide, green to yellow, scar absent, operculum conical to rounded sometimes apiculate, stamens inflexed or irregularly flexed, anthers reniform to cordate, versatile, dorsifixed, dehiscing by confluent slits (usually), style short or long, stigma tapered, locules 3 or 4, the placentae each with 2 vertical ovule rows. Flowers white.
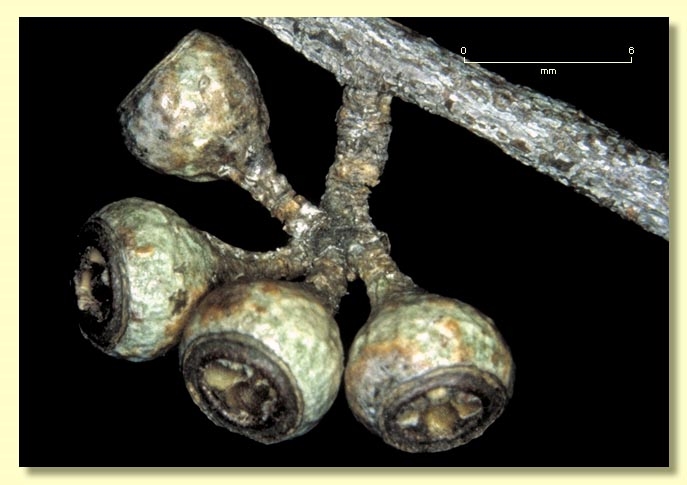
Fruit sessile or pedicellate (pedicels to 0.5 cm long), cup-shaped, obconical or hemispherical, 0.3–0.7 cm long, 0.4–0.8 cm wide, disc slightly raised to slightly descending, valves 3 or 4, near rim level.
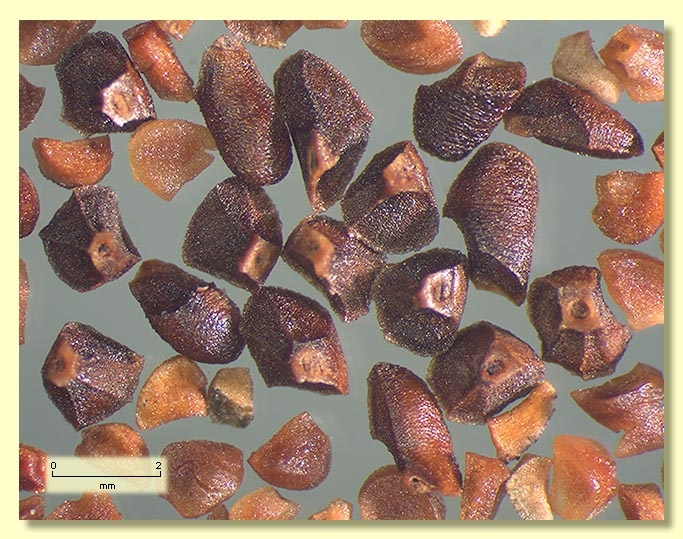
Seeds brown or reddish brown, 1.5–2.5 mm long, pyramidal or obliquely pyramidal, dorsal surface smooth, hilum terminal.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons reniform; stems rounded in cross-section, warty or smooth, slightly glaucous; leaves sessile and opposite for many nodes, cordate to ovate, 5–8 cm long, 3–5.5 cm wide, bases amplexicaul or connate, dull, glaucous or grey-green.
Flowering has been recorded in January, May, June, July, September, October, November and December.
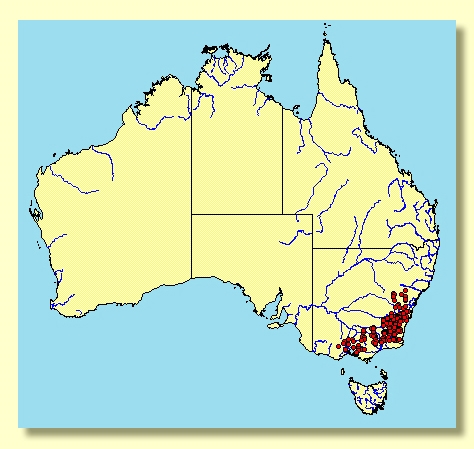
A small to medium-sized peppermint tree widespread from south of the Glen Morrison and Niangala area of the Northern Tablelands of New South Wales through the Southern Tablelands to eastern Victoria, often on poor shallow soils.
Among the peppermints E. dives is notable for the very conspicuous, opposite, ovate, sessile, glaucous juvenile leaves which are, rarely, slightly connate at their bases. The adult leaves are broad, green and when fully adult glossy. They differ from the other broad-leaved peppermint, E. croajingolensis, of eastern Victoria and just into New South Wales, which has a conspicuous bluish adult crown with leaves that are notably pendulous on saplings.
Eucalyptus dives belongs to Eucalyptus subgenus Eucalyptus section Aromatica (the peppermints) because the buds have a single operculum, anthers are reniform, ovules are in two rows, seeds are ± pyramidal, adult leaf venation is acute and juvenile leaves are sessile and opposite for many pairs. Within this section five closely related species form series Radiatae, viz. E. elata, E. radiata (with three subspecies), E. croajingolensis, E. willisii (with two subspecies), and E. dives. They differ from each other in bark and leaf characteristics, and, as a group, series Radiatae differs from the endemic Tasmanian peppermints, series Insulanae, by having numerous oil glands in the juvenile leaves.