Eucalyptus | Symphyomyrtus | Maidenaria | Triangulares | Acaciiformes
Euclid - Online edition
Eucalyptus fulgens
T: 0.9 km along Red Hill Road from the intersection of Albers and Mainstar roads, Upper Beaconsfield, Victoria, 20 Jun. 1994, K.Rule 9464; holo: MEL.
Bark rough usually to small branches, thick, fibrous, furrowed longitudinally, dark-grey; branches < 8cm diameter sometimes smooth.
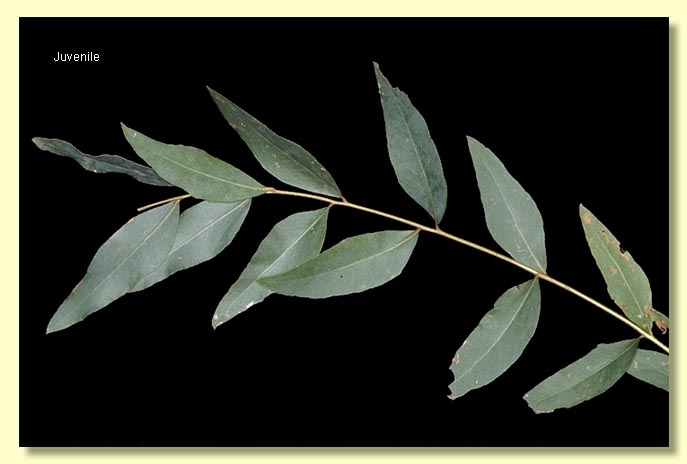
Juvenile growth (coppice or field seedlings to 50 cm): stem rounded or square in cross-section, warty or smooth; juvenile leaves opposite and sessile to shortly petiolate for 6 to 12 nodes then becoming alternate, elliptical to lanceolate, 4–10.5 cm long, 1.8–3.5 cm wide, base usually tapering to petiole, blue-green and crenulate at first but soon green and with entire margin.
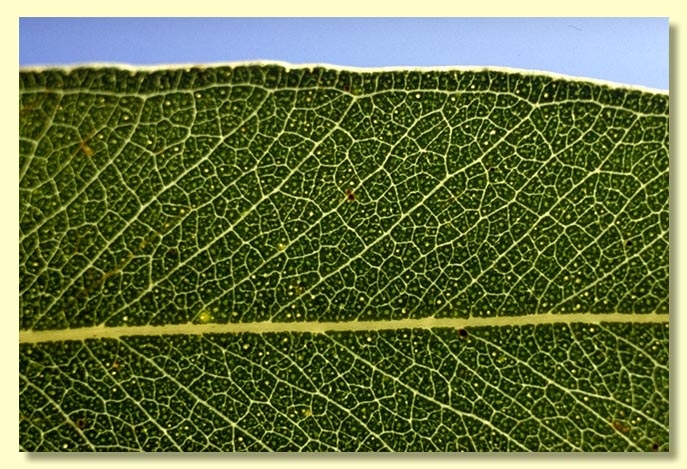
Adult leaves alternate, petiole 1–3.5 cm long; blade lanceolate to falcate, 9–24.5 cm long, 1.3–4 cm wide, base tapering to petiole, concolorous, glossy, green, side-veins usually greater than 45° to midrib, moderately to densely reticulate, intramarginal vein parallel to and well removed from margin, oil glands mostly island.
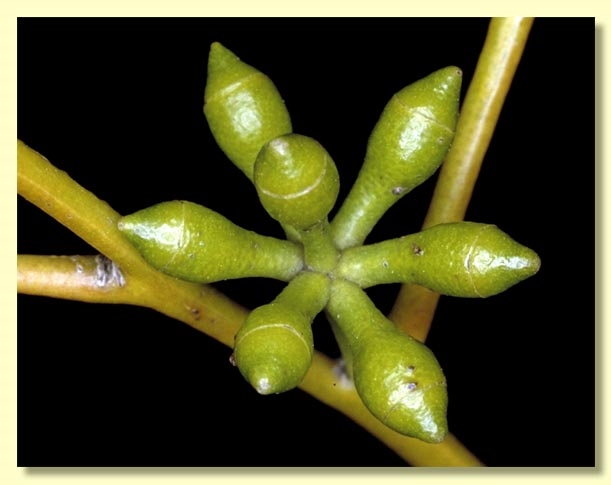
Inflorescence axillary unbranched, peduncles 0.2–0.9 cm long, buds 7 per umbel, pedicels 0.2–0.4 cm long. Mature buds ovoid to fusiform, 0.4–0.6 cm long, 0.3–0.4 cm wide, green, scar present, operculum conical, stamens inflexed, anthers cuboid to oblong, versatile, dorsifixed, dehiscing by longitudinal slits (non-confluent), style long, stigma blunt, locules 3 or 4, the placentae each with 4 vertical ovule rows. Flowers white.
Fruit pedicellate (pedicels 0.1–0.4 cm long), hemispherical or cup-shaped, 0.3–0.4 cm long, 0.4–0.6 cm wide, disc level, or disc raised-convex, annular or oblique, valves 3 or 4, near rim level or slightly exserted.
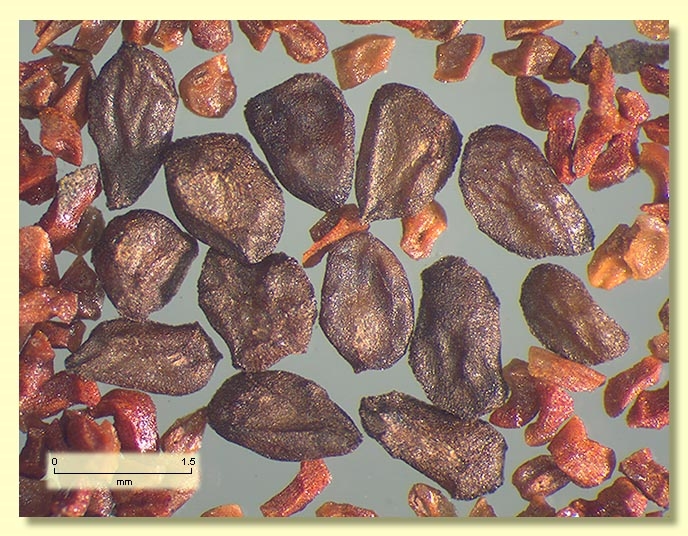
Seeds dark brown to black or grey, 1.2–2 mm long, ovoid or flattened-ovoid, often pointed at one end, surface more or less smooth, dorsal surface usually lacunose, hilum ventral.
Cultivated seedlings (measured at ca node 10): cotyledons bilobed to oblong; stems rounded or square in cross-section, smooth or slightly warty; leaves sessile, opposite and elliptic for ca 7 to 10 nodes, becoming alternate, shortly petiolate, ovate, 4–7 cm long, 1.2–3.2 cm wide, base rounded to tapering, margin entire or subcrenulate, apex rounded to pointed, dull, green.
Flowering has been recorded in January and March.
A small to medium-sized tree of restricted distribution on heavy soils over sandstone east of Melbourne, Victoria, from east of Healesville and Woori Yallock to the Latrobe Valley near Driffield. E. fulgens has deeply furrowed rough bark like an ironbark and glossy green adult leaves.
Eucalyptus fulgens belongs in Eucalyptus subgenus Symphyomyrtus section Maidenaria, a large group of species more or less restricted to south-eastern Australia, characterised by bilobed cotyledons, simple axillary inflorescences, buds with two opercula, stamens with versatile anthers and flattened seeds with a ventral hilum. Within this section E. fulgens and five other species form series Acaciiformes diagnosed by the rough bark, juvenile leaves that are soon alternate, glandular adult leaves, non-swampy habitat, and small, rather flat-topped fruit. Three of these species, E. fulgens, E. aromaphloia and E. ignorabilis, are restricted to Victoria and far south-eastern New South Wales. The latter two species have dull adult leaves, not glossy. The remaining species in series Acaciiformes are E. acaciaformis, E. nicholii and E. corticosa, all from north-eastern New South Wales and all having linear-lanceolate seedling leaves.