Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants - Online edition
Cinnamomum oliveri F.M.Bailey
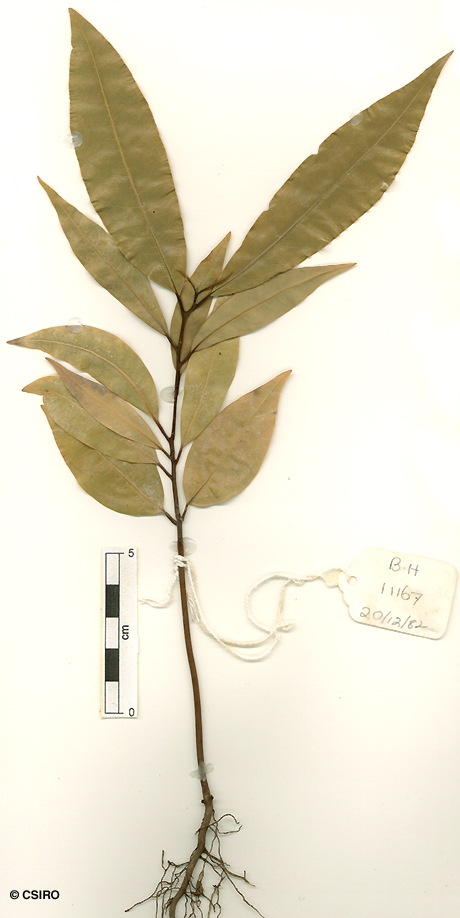
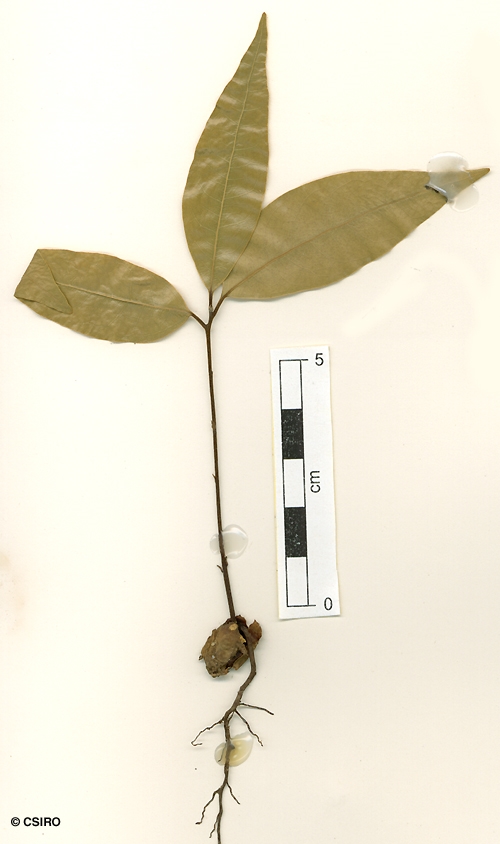



Bailey, F.M. (1892) Queensland Department of Agriculture and Stock. Botany Bulletin 5: 24. Type: Maroochie, F. M. Bailey?, J. D. Low; holo: (BRI 23599).
Cinnamonwood; Black Sassafras; Camphorwood; Oliver's Bark; Sassafras; Sassafras, Black; Sassafras, Oliver's; Oliver's Sassafras
Strong sarsaparilla odour in the blaze.
Tepals about 3-4.1 mm long. Stamens nine (six opening inwards and three opening outwards). Staminodes three.
Fruiting receptacle or cupule entire at the apex. Fruits about 18 x 14 mm when ripe.
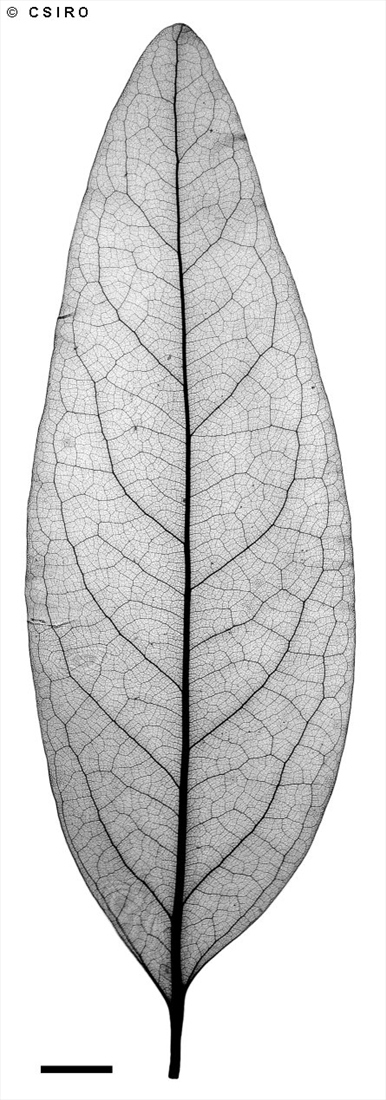
At the tenth leaf stage: leaf blade penninerved, slightly glaucous on the underside; oil dots small, visible with a lens. Seed germination time 21 to 39 days.
Endemic to Australia, occurs in CYP, NEQ, CEQ and southwards to south-eastern New South Wales. Altitudinal range from sea level to 1000 m. Grows in well developed rain forest on a variety of sites but tending to favour the drier or more seasonal rain forests in CYP and NEQ. This species is rarely encountered in NEQ.
Food plant for the larval stages of the Blue Triangle Butterfly. Common & Waterhouse (1981).
This species may have medicinal properties.
The bark has a strong aromatic perfume and a 9% tannin content which made it astringent. For these two reasons it was used as a relatively pleasant diarrhoea treatment, and was prescribed as such by doctors of the late nineteenth century. Cribb (1981).
This species produces millable logs and the sawn timber is marketed as Camphorwood, a useful general purpose timber. Wood specific gravity 0.56-0.66. Hyland (1989).





