Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants - Online edition
Duboisia myoporoides R.Br.
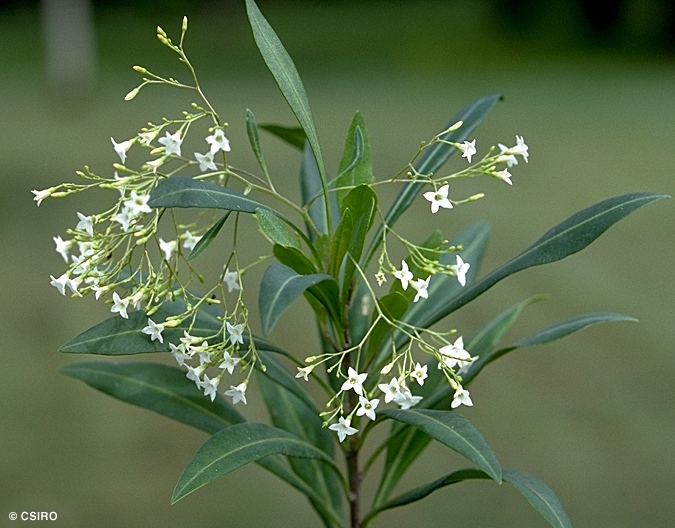
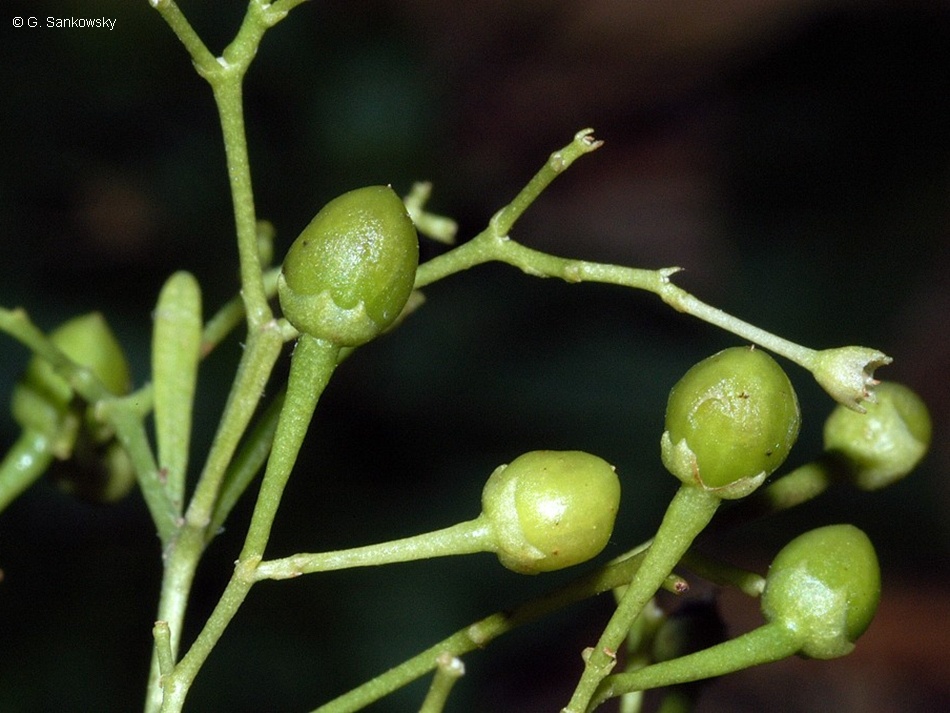





Brown, R. (1810) Prodromus Florae Novae Hollandiae : 448. Type: New South Wales, Port Jackson, R. Brown, syn: BM, K, MEL, NSW, P. (Fide Purdie et al. 1982.).
Soft Corkwood; Mgmeo; Poison Corkwood; Poisonous Corkwood; Corkwood Tree; Eye-opening Tree; Eye-plant; Duboisia; Yellow Basswood; Elm; Corkwood
Leaf blades about 4-12 x 0.8-2.5 cm, soft and fleshy, indistinctly veined. Midrib raised on the upper surface.
Small bell-shaped flowers present during most months of the year. Calyx about 1 mm long, lobes short, less than 0.5 mm long. Corolla induplicate-valvate in the bud. Induplicate sections of the corolla and inner surfaces of the corolla lobes clothed in somewhat matted, stellate hairs. Corolla tube about 4 mm long, lobes about 2 mm long.
Cotyledons narrowly elliptic to almost linear, about 5-8 mm long. First pair of true leaves obovate, margins entire. At the tenth leaf stage: leaf blade +/- spathulate, apex rounded, base attenuate; midrib raised in a channel on the upper surface; petiole with a ridge down the middle. Seed germination time 31 to 264 days.
This species is rich in alkaloids and the leaves have been harvested commercially for the extraction of scopalamine. Cases of poisoning have been reported in cattle, horses and humans. Everist (1974).
This species may have medicinal properties. It is also poisonous.
Duboisia is probably the most important of the Australian native medicinal plants. The leaves are a valuable source of the alkaloid drugs, scopolamine and hyoscyamine. Cribb (1981).





